Select Columns
Manual selection of data attributes and composition of data domain.
Inputs
- Data: input dataset
- Features: list of attributes
Outputs
- Data: dataset with columns as set in the widget
- Features: list of attributes
The Select Columns widget is used to manually compose your data domain. The user can decide which attributes will be used and how. Orange distinguishes between ordinary attributes, (optional) class attributes and meta attributes. For instance, for building a classification model, the domain would be composed of a set of attributes and a discrete class attribute. Meta attributes are not used in modeling, but several widgets can use them as instance labels.
Orange attributes have a type and are either discrete, continuous or a character string. The attribute type is marked with a symbol appearing before the name of the attribute (D, C, S, respectively).
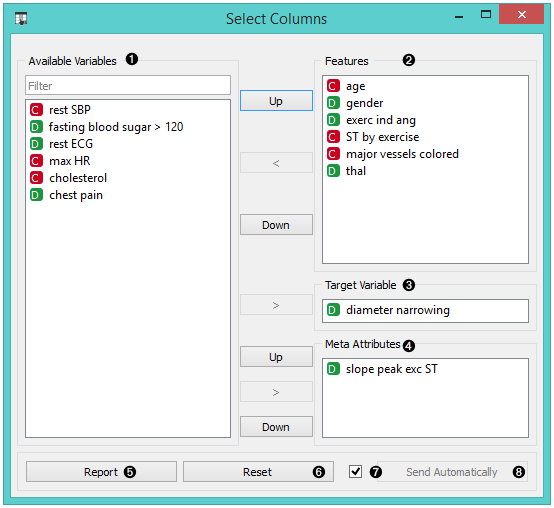
- Left-out data attributes that will not be in the output data file. Use Filter to find (and include) ignored features.
- Data attributes in the new data file. Use Filter to find (and exclude) used features.
- Target variable (categorical or numeric). If none, the new dataset will be without a target variable. Only a single target variable is accepted.
- Meta attributes of the new data file. These attributes are included in the dataset but are, for most methods, not considered in the analysis.
- Reset the domain composition to that of the input data file. When the widget receives data with additional columns they are added to the Ignored features if Ignore new variables by default is checked. Tick Send Automatically if you wish to auto-apply changes of the data domain.
The widget enables filtering on widget names.
Examples
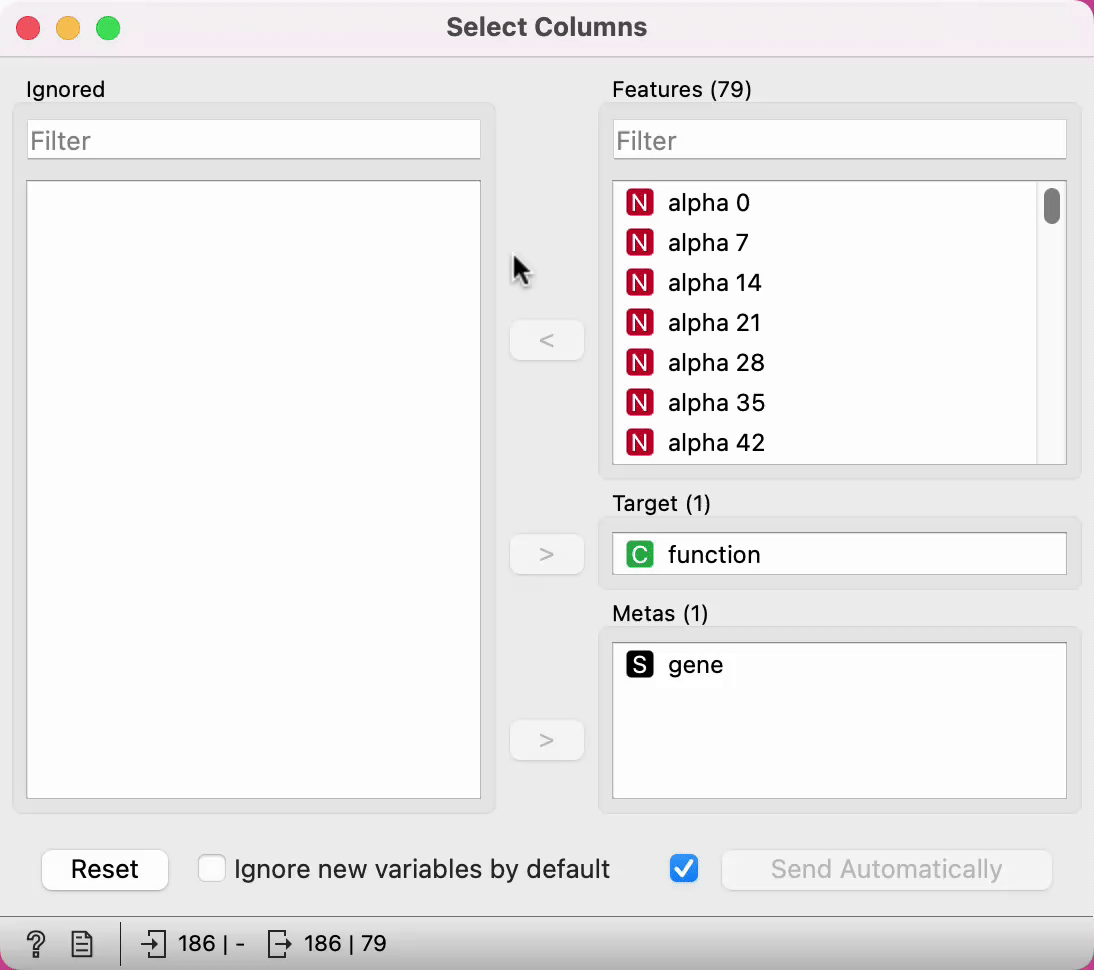
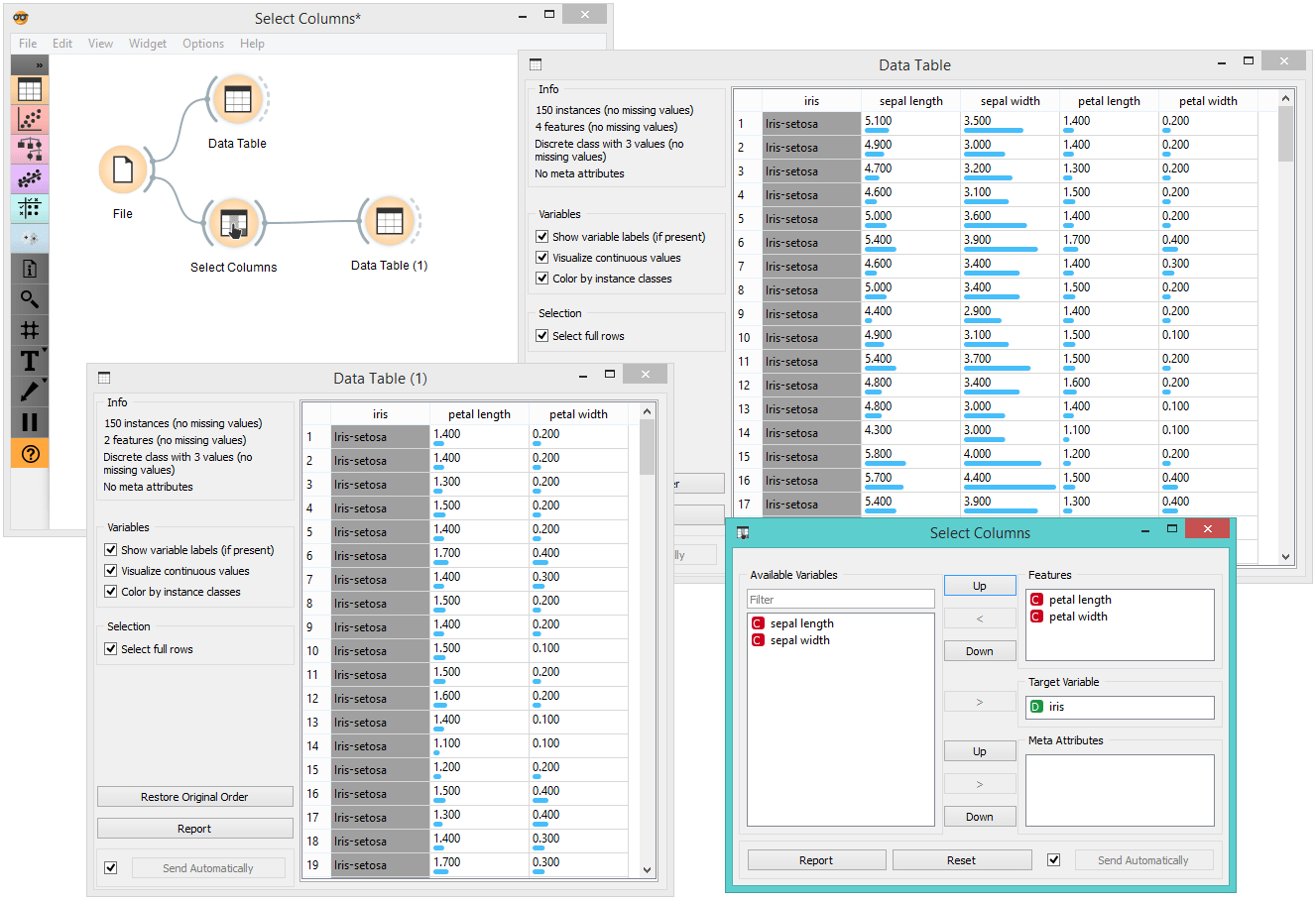
In the workflow below, the Iris data from the File widget is fed into the Select Columns widget, where we select to output only two attributes (namely petal width and petal length). We view both the original dataset and the dataset with selected columns in the Data Table widget.
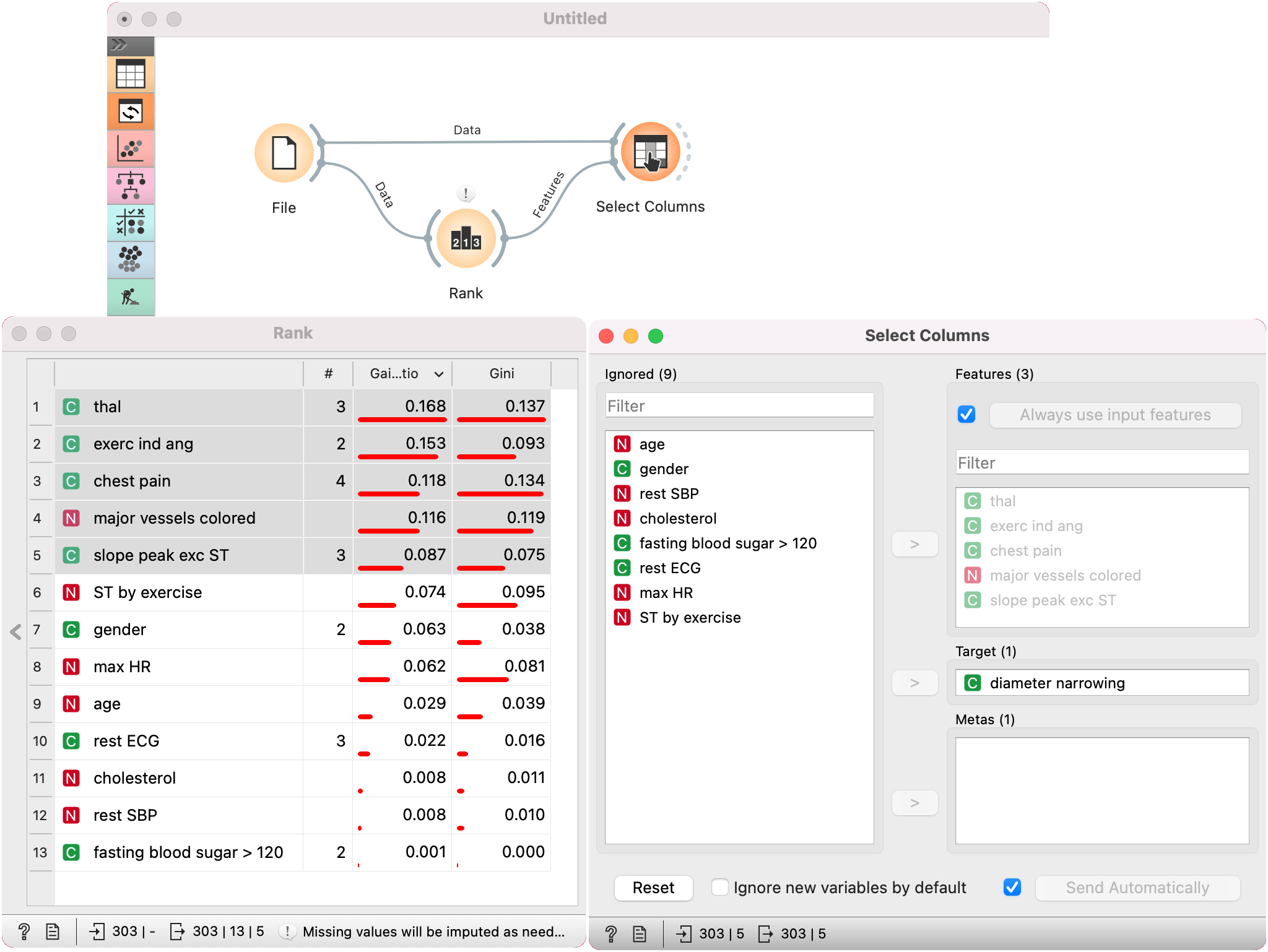
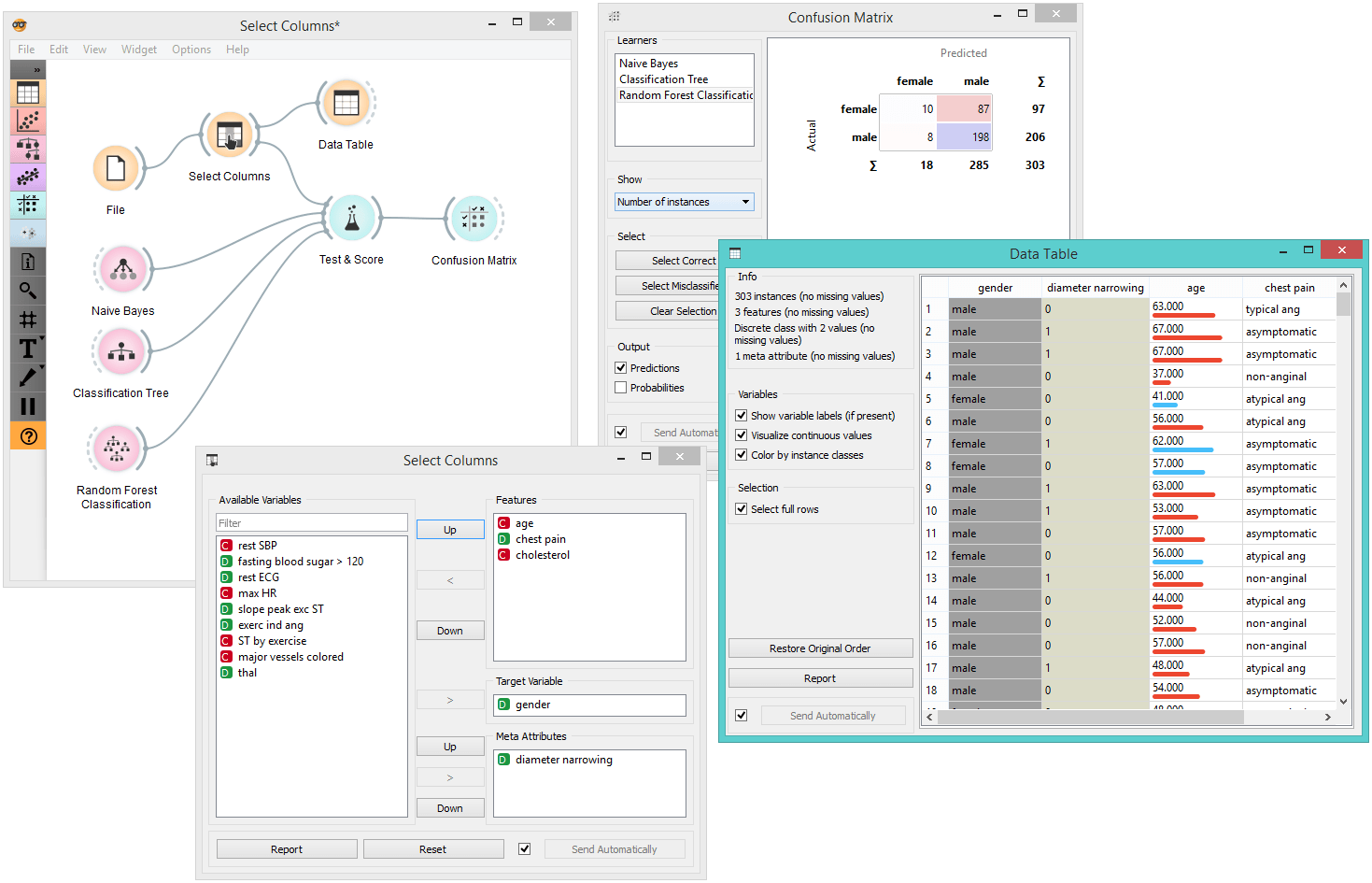
For a more complex use of the widget, we composed a workflow to redefine the classification problem in the heart-disease dataset. Originally, the task was to predict if the patient has a coronary artery diameter narrowing. We changed the problem to that of gender classification, based on age, chest pain and cholesterol level, and informatively kept the diameter narrowing as a meta attribute.
Another option is to pass a list of features for Select Columns to use. We are using heart-disease dataset for this example. With Rank, we have ranked the features by their gain ratio and selected the best scoring 5 features. Next, we pass the list of features to Select Columns. Selected features are automatically passed to the Features box. We have ticked Use input features, we gives precedence to the input feature list.