Continuize
Turns categorical variables (attributes) into numeric ("continuous") dummy variables.
Inputs
- Data: input data set
Outputs
- Data: transformed data set
The Continuize widget receives a data set in the input and outputs the same data set in which some or all categorical variables are replaced with numeric (continuous) ones and numeric variables are scaled.
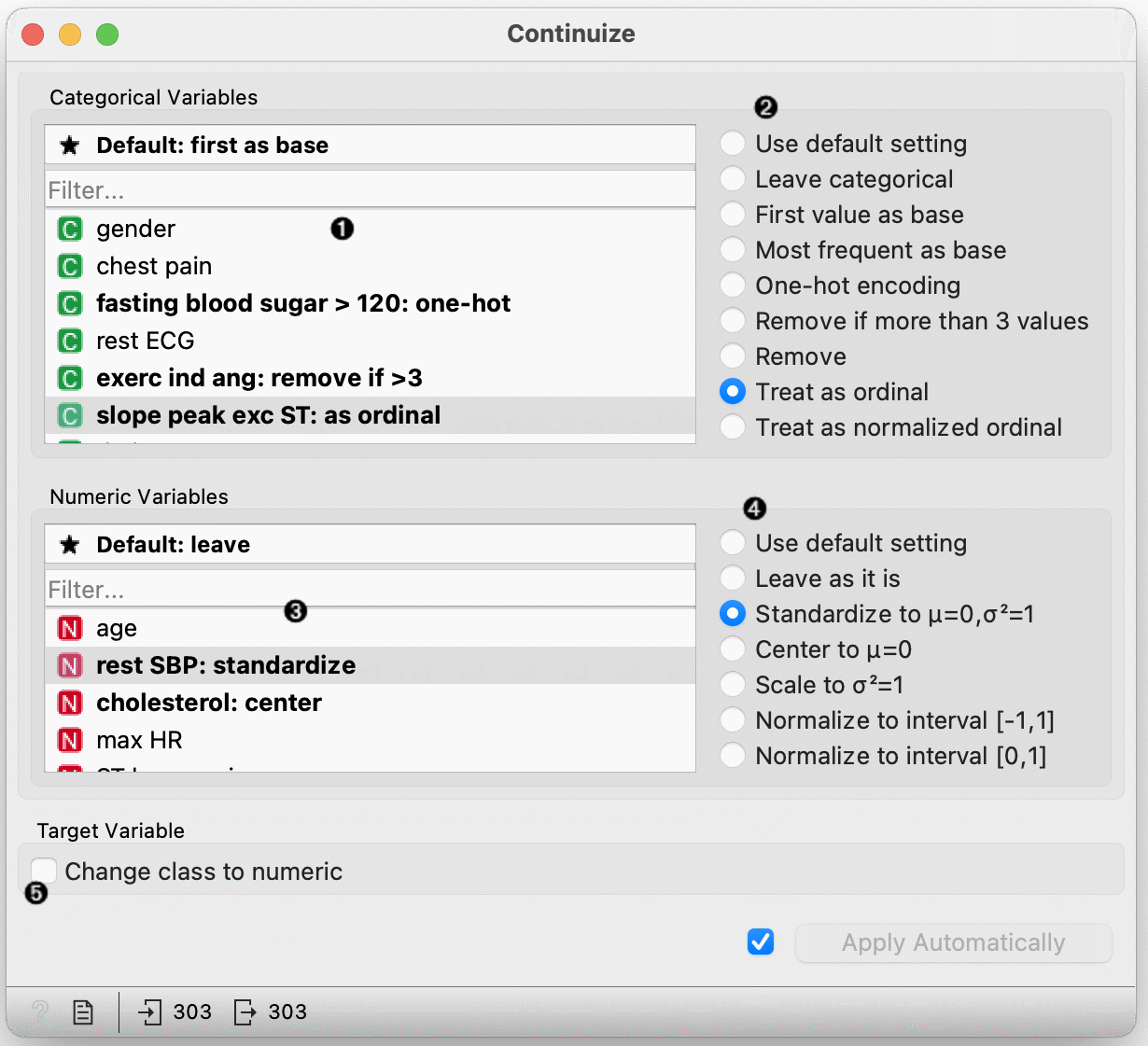
- Select a categorical attribute to define its specific treatment, or click the "Use default setting" option above to set the default treatment for all categorical attributes without specific settings. Multiple attributes can be chosen.
- Define the treatment of categorical variables.
Examples in this section will assume that we have a categorical attribute status with values low, middle and high, listed in that order. Options for their transformation are:
- Use default setting: use the default treatment.
- Leave categorical: leave the attribute as it is.
- First value as base: a N-valued categorical variable will be transformed into N-1 numeric variables, each serving as an indicator for one of the original values except for the base value. The base value is the first value in the list. By default, the values are ordered alphabetically; their order can be changed in Edit Domain. In the above case, the three-valued variable status is transformed into two numeric variables, status=middle with values 0 or 1 indicating whether the original variable had value middle on a particular example, and similarly, status=high. Status=low is indicated by both values being 0.
- Most frequent value as base: similar to the above, except that the most frequent value is used as a base. So, if the most frequent value in the above example is middle, then middle is considered as the base and the two newly constructed variables are status=low and status=high.
- One-hot encoding: this option constructs one numeric variable per each value of the original variable. In the above case, we would get three variables, status=low, status=middle and status=high.
- Remove if more than 2 values: removes non-binary categorical variables from the data.
- Remove: removes the attribute.
- Treat as ordinal: converts the variable into a single numeric variable enumerating the original values. In the above case, the new variable would have the value of 0 for low, 1 for middle and 2 for high. Again note that the order of values can be set in Edit Domain.
- Treat as normalized ordinal: same as above, except that values are normalized into range 0-1. In our example, the values of the new variable would be 0, 0.5 and 1.
- Select attributes for individual treatment or click "Default" to set the default treatment for numeric attributes.
- Define the treatment of numeric attributes.
- Use default setting: use the default treatment.
- Leave as it is: do not change anything.
- Standardize: subtract the mean and divide by the standard deviation (not available for sparse data).
- Center: subtract the mean (not available for sparse data).
- Scale: divide by standard deviation.
- Normalize to interval [-1, 1]: linearly scale the values into interval [-1, 1] (not available for sparse data)
- Normalize to interval [0, 1]: linearly scale the values into interval [0, 1] (not available for sparse data)
- Reset All resets all variables to default option. If Apply automatically is ticked, changes will be communicated automatically. Alternatively, click Apply.
Examples
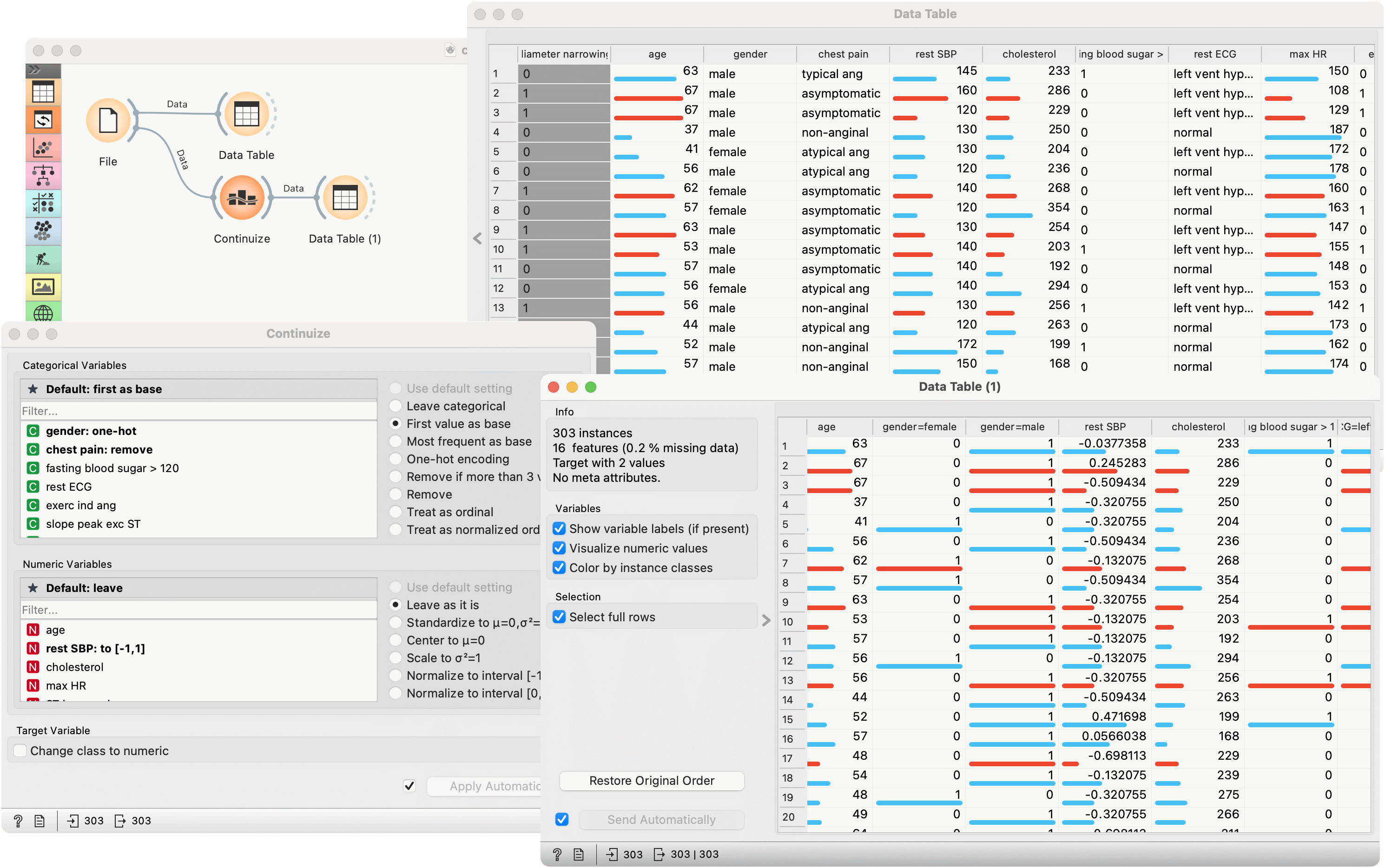
First, let's see what is the output of the Continuize widget. We feed the heart_disease data from the File into the Data Table and see how it looks like. Then we continuize the categorical variables using various options and observe them in another Data Table.
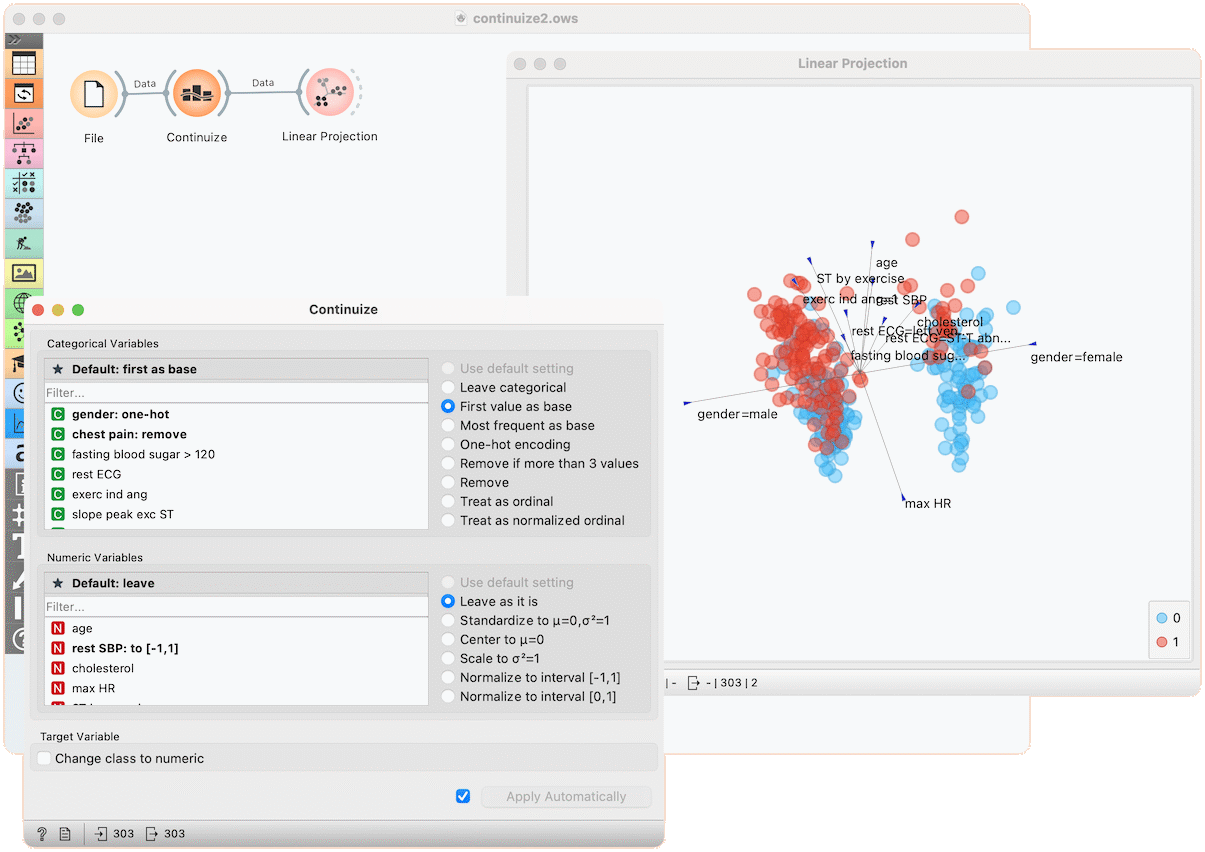
In the second example, we show a typical use of this widget - in order to properly plot the linear projection of the data with the Linear Projection widget, categorical attributes need to be converted to numeric ones and that is why we put the data through the Continuize widget before drawing it. Gender, for instance, is transformed into two attributes "gender=female" and gender=male.