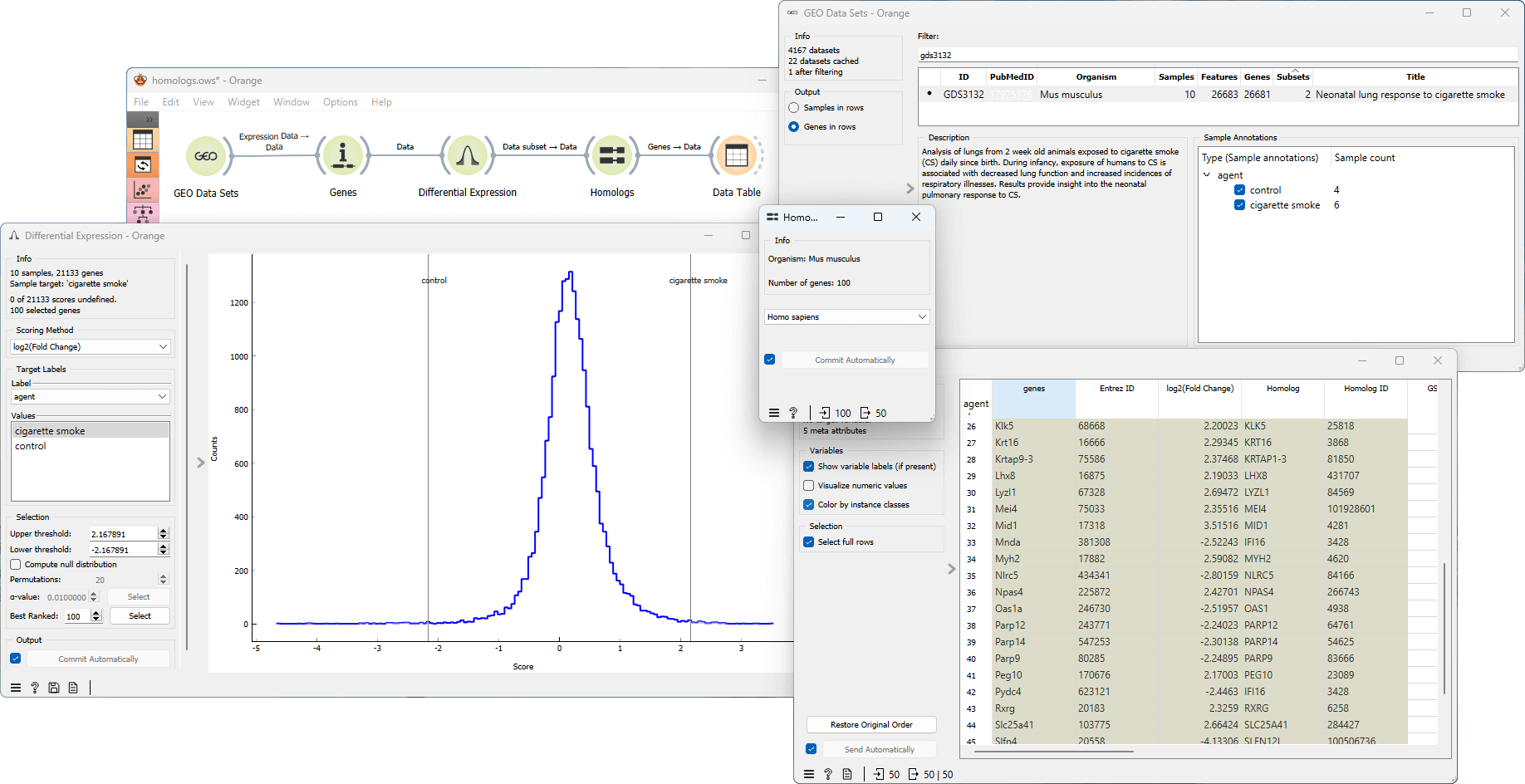
Homologs
Finds homologs to genes in the input data set.
Inputs
- Data: Input data set.
Outputs
- Genes: List of homologs.
The Homologs widget finds homologs to genes in the input data set for the selected organism. Homologs are genes or proteins that share a common ancestry, often found in different species, and may have similar functions or sequences. Studying homologs is useful because it provides insights into evolutionary relationships, gene function, drug discovery, and aids in comparative genomics and experimental design
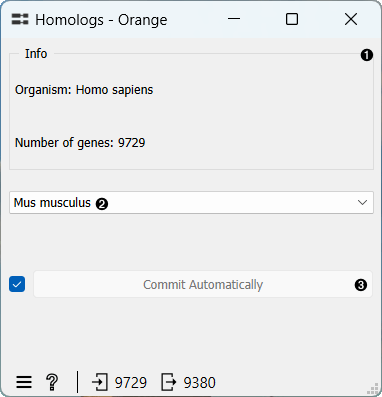
- Information on the organism and the number of genes in the input data.
- Choose the organism for which you wish to identify homologs.
- If Commit Automatically is ticked, results will be automatically sent to the output. Alternatively, press Commit.
Example
From the GEO Data Sets widget we select the GDS3132 gene expression data set for neonatal lung response to cigarette smoke profiling in mice (Mus musculus). Next, we annotate the genes using the Genes widget. We then connect the Genes and Differential Expression widgets to inspect the differentially expressed genes. We select the top 100 genes and feed the data to Homologs widget and select the organism of interest, in our case Homo Sapiens. The output is a list of homologs to the genes in the input data set. Next, we connect the Homologs widget to the Data Table widget. This allows us to efficiently inspect and work with information specifically related to homologous genes. This workflow can be accessed here.